Your Medicare Part B costs should include monthly premiums, an annual deductible, and co-insurance for covered services.
Whether you are automatically enrolled in Medicare Part B (medical insurance) or you sign up, you will have several costs associated with your coverage. This includes deductibles, premiums, and coinsurance. However, these costs can vary based on a variety of factors.
Read to understand the costs associated with Medicare Part B, as well as what Part B covers and how to enroll.
How much does Part B cost?
Medicare Part B covers a variety of doctor and medical services and supplies you may need. Costs include a monthly premium, an annual deductible, and coinsurance for most services and supplies.
Monthly premium
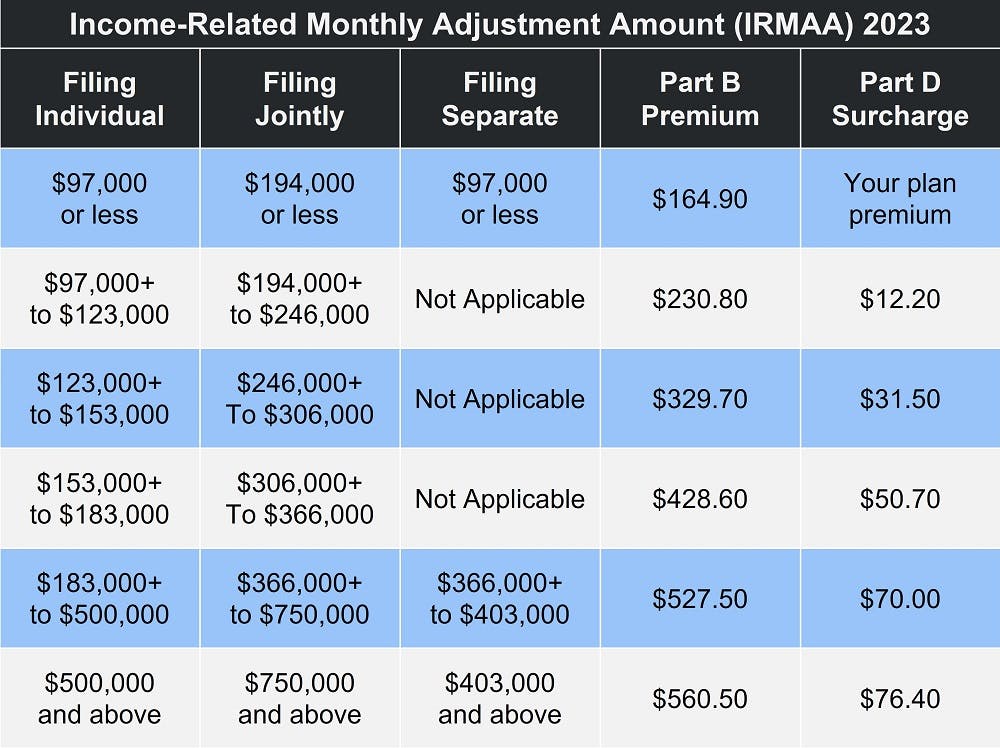
You pay a premium to Medicare each month for Part B coverage. In 2023, the standard premium amount is $164.90. This will be automatically deducted from either:
- Social Security,
- Railroad Retirement Board (RRB), or
- Office of Personnel Management
If you don’t receive any of these payments, you’ll get a bill.
If your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) as reported on your IRS tax return from two years ago is more than a certain amount, you’ll have to pay the standard premium plus an Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA).
Medicare Part B Premium Give-Back Plan
Some Medicare Advantage Plans offer a Part B premium reduction benefit, or premium give back. When you enroll in the policy, the carrier either pays part of or the whole premium for your Part B outpatient coverage. This reduces the amount you pay for your Part B premium, and the MA plan covers the remainder.
Not every plan or every state offers this capability, and you are only eligible if you pay your own Part B premium, meaning you don't have Medicaid or other forms of assistance that could pay your premium for you. You must also be enrolled in Part A and Part B. The plan's Evidence of Coverage outlines how much of a reduction is available.
Additionally, the plan only participates with Social Security, so you'd see the reduction on the amount taken out of your Social Security check.
The amount you'd get back could range from $0.10 up to your full premium ($164.90 in 2023). It depends on the options available in your area, as well as your plan.
Note that it could take Social Security one to three months to begin your Part B premium rebate, but after the rebate takes effect, you'll see an increase in your check total.
Part B deductible
In 2023, you’ll pay $226 for your Part B deductible. This is the amount you have to pay out-of-pocket before Medicare begins to pay for services and supplies.
Part B coinsurance
Once you meet your deductible, you’ll typically pay 20 percent of the Medicare-approved amount for:
- Most doctor services, including while you’re a hospital inpatient
- Outpatient therapy and services
- Durable medical equipment (DME)
Medicare will pay the other 80 percent.
Other costs for Medicare-approved services include:
- $0 for clinical laboratory services
- $0 for home health care services
- $0 for covered annual preventive screenings
- 20 percent for outpatient mental health services, including visits to your doctor to diagnose or treat your condition
undefined - A percentage of the Medicare-approved amount for each service you get from a doctor for partial hospitalization mental health services (as long as the doctor accepts assignment)
undefined - Hospital copayment for each service you get in a hospital outpatient setting, except for certain preventive services
There is no limit on Part B coinsurance costs, so these out-of-pocket costs can add up if you visit the doctor often or need other services or supplies.
Late enrollment penalty
If you do not enroll in Part B when eligible. Your monthly premium may go up 10 percent for each 12-month period you could have had Part B but didn’t. In most cases, you’ll have to pay this penalty each time you pay your premiums for as long as you have Part B, and it could increase the longer you go without coverage. This is a life-long penalty.
What does ‘accept assignment’ mean?
Doctors or other healthcare providers or durable medical equipment suppliers must accept assignment in order for the services or supplies to be covered by Medicare. This means they agree to accept the amount that Medicare will pay for a visit or service, known as the Medicare-approved amount, as payment in full.
This helps to reduce out-of-pocket costs for you. Providers that do not accept assignment can charge up to 15 percent more than the Medicare-approved amount, so you’d have to pay the 20 percent coinsurance plus up to an extra 15 percent.
Additionally, providers can opt out completely of a Medicare program, which means they can charge whatever they want for services or supplies and will not bill Medicare. This means you’d have to pay the full cost out-of-pocket, and nothing will be covered by Medicare.
To protect your wallet, make sure providers or suppliers you see accept assignment.
What does Medicare Part B cover?
Part B covers medically necessary services or supplies that are needed to diagnose or treat a medical condition, as well as preventive services to help keep you healthy longer. Typically, this includes:
- Doctor visits
- Outpatient care, such as emergency room services and same-day surgical procedures
- Lab tests and services
- Diagnostic imaging
- Therapy (physical, occupational, speech-language)
- Diabetes supplies
- Clinical research
- Ambulance services
- Durable medical equipment (DME)
- Mental health services (both inpatient and outpatient)
- Certain prescription medications
- Chemotherapy and radiation
- Annual screenings
To understand if Medicare Part B covers what you need, talk to your doctor or healthcare provider. In most cases, the services and supplies must be medically necessary to be covered, so check with your doctor that that’s the case.
You can also contact Medicare directly.
How to apply for Medicare Part B
There are a few times per year you can enroll in Medicare called enrollment periods.
Initial Enrollment Period
If you’re eligible for Medicare when you turn 65, you are able to sign up during your Initial Enrollment Period. This is a 7-month period surrounding your birthday, including the three months before the month you turn 65, the month you turn 65, and the three months after the month you turn 65.
You can decline Part B if you have group health insurance from an employer you or your spouse is actively working at, and that insurance is primary to Medicare, meaning it pays before Medicare does. Remember, if you do not sign up for Part B when you’re eligible and you do not have other coverage in place, you’ll have to pay a late enrollment period.
Special Enrollment Period (SEP)
If you don’t enroll in Part B during your Initial Enrollment Period, you may have an opportunity to enroll during a Special Enrollment Period. However, you must meet certain requirements to be eligible.
If you enroll during an SEP, your coverage will begin the month after Social Security gets your completed request.
You are not eligible for an SEP if you have COBRA or retiree health plan coverage that ends, if you have Veterans Affairs or Individual Health Insurance Marketplace coverage, or if you have End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).
General Enrollment Period (GEP)
If you don’t enroll when you’re first eligible, and you don’t qualify for an SEP, you can still enroll during the Medicare General Enrollment Period, from January 1 through March 31. In this case, coverage will begin July 1 of that year.
In most cases, if you enroll during the GEP, you will have to pay a late enrollment penalty for as long as you have Part B.
How to enroll
To enroll in Medicare, you can:
- Apply online at www.ssa.gov.
- Visit your local Social Security office.
- Call Social Security.
- Call the RRB (if you worked for a railroad).
- If you already have Part A and want Part B, you must complete an Application for Enrollment in Part B.
Eligibility for Medicare Part B
If you are eligible for premium-free Part A, you are also eligible for enrollment in Part A as soon as you are entitled to Part A.
If you must pay a premium for Part A, you are eligible for Part B if:
- Be age 65 or older;
- Be a U.S. resident; AND
- Be either a U.S. citizen or an alien who has been lawfully admitted for permanent residence and has been residing in the U.S. for five continuous years.
Additional resources
Medicare.gov: Medicare Costs At a Glance
External website link
ClearMatch Medicare: Medicare Part B Late Enrollment Penalty
Internal website link
ClearMatch Medicare: Medicare Part B Excess Charges
Internal website link



