All U.S. citizens aged 65 and older qualify for Medicare, regardless of income.
We want to start by saying that Medicare eligibility is not based on income. If you are an American citizen age 65 or older, you qualify for Medicare. How much money you do or do not make plays no part. Some people confuse Medicare with Medicaid, which does have an income requirement. Medicare is a federal health insurance program whereas Medicaid is managed at the state level.
That said, income does play a role in determining whether you qualify for certain benefits within the Medicare program, such as Extra Help. In addition, if your income exceeds thresholds set by Social Security, your monthly premiums may be higher.
How Do You Qualify for Medicare?
The majority of beneficiaries – around 85 percent – qualify for Medicare based on their age. All American citizens aged 65 or older can sign up for Medicare.
You may also be entitled to Medicare if you have a disability and qualify for either Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) or Social Security benefits for 24 months. Finally, you may be eligible for Medicare if you have been diagnosed with either amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Income has no bearing on Medicare eligibility.
Does Income Affect Medicare Part A Premiums?
Medicare Part A, also known as hospital insurance, covers inpatient care. The vast majority of Medicare beneficiaries paid payroll taxes for the required 40 quarters (10 years) to qualify for premium-free Part A. Even if you do have a Medicare Part A premium, though, you won't pay more based on your income.
If you or your spouse did not work and pay Medicare taxes for the required 40 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $506 per month in 2023.
How Income Affects Medicare Part B Premiums
Medicare Part B is also known as medical insurance. It covers services like doctor visits and lab work. The standard Medicare Part B premium is $164.90 per month in 2023.
Unlike Part A, you may pay higher premiums for Part B if your income exceeds certain thresholds set by the Social Security Administration (SSA). This surcharge is called the Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA).
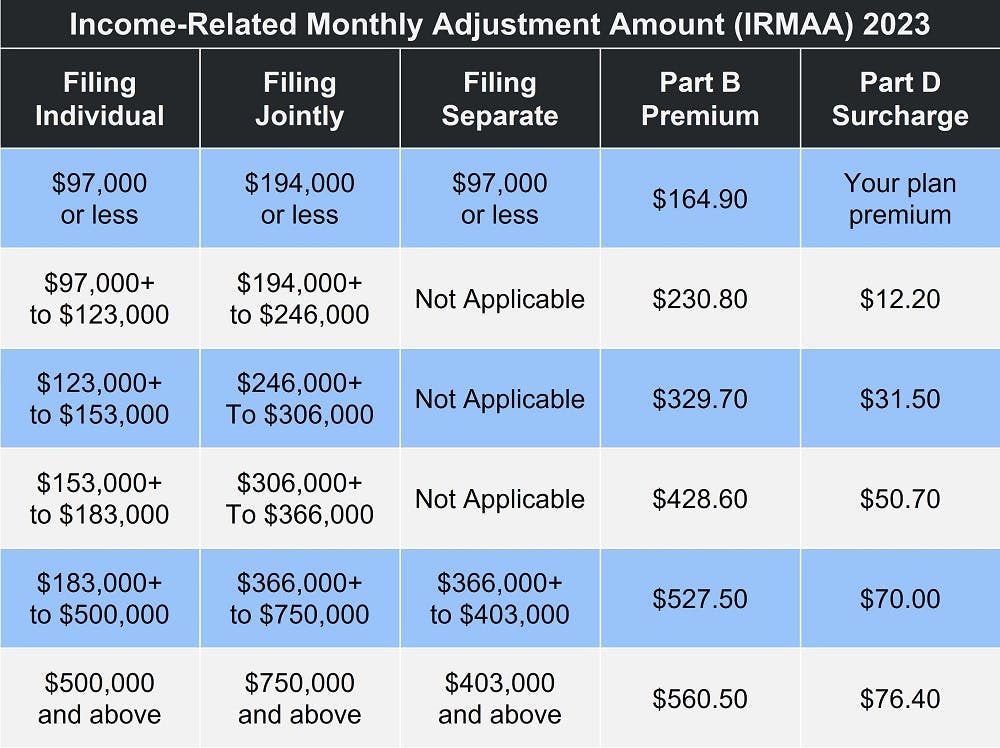
Most Medicare beneficiaries pay the standard Part B premium. You only pay a surcharge if your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) from two years ago is over $97,000 (filing as an individual) or $194,000 (married filing jointly). The image to the left details the premium surcharge at each income level.
The image below demonstrates the IRMAA income thresholds for 2023.
How Income Affects Medicare Part D Premiums
Original Medicare does not include prescription drug coverage. These benefits are available through a Medicare Part D prescription drug plan (PDP). You may join either a standalone Part D plan or a Medicare Advantage Prescription Drug plan (MA-PD).
Private insurance companies provide Part D plans, which means premiums vary. But as with Part B, your monthly Medicare Part D premium may include a surcharge if your income exceeds the limits listed above. The image to the right details the Medicare Part D IRMAA.
How Medicare Determines IRMAA
Medicare premiums are based on the adjusted gross income you reported to the IRS two years ago. You will receive the IRMAA notification from Social Security if your MAGI exceeds the amounts listed above.
Since the Income Related Monthly Adjustment Amount is based on your tax return from two years ago, it's possible your income is no longer that high – particularly if you retired. You may file an appeal if you believe the IRMAA is unwarranted. However, you have to prove that there has been a permanent reduction in income, typically due to a life-changing event (such as retirement or the death of a spouse).
Find full details at Medicare.gov by clicking here.
How to Qualify for Help Paying Your Medicare Parts A and B Costs
There are four Medicare Savings Programs designed to help beneficiaries pay their Medicare costs. This may include deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments. Guidelines for each program vary.
Resources that count toward program limits include:
- Checking and savings accounts
- Stocks
- Bonds
Resources that do not count include:
- Your home
- One vehicle
- A prepaid burial plot and/or up to $1,500 in burial expenses (assuming the funds have been set aside for that purpose)
- Household furniture and personal items
The following information is for the contiguous United States. If you live in Hawaii or Alaska, resource limits are slightly higher.
Check with your state's Medicaid program to see if you qualify for any of the following:
Qualified Medicare Beneficiary (QMB) Program
Monthly income and resource limits for the QMB Program are:
- Filing individually: $1,153 monthly income; $8,400 in resources
- Married filing jointly: $1,546 monthly income; $12,600 in resources
This program helps pay your premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance for both Medicare Part A and Medicare Part B.
If you qualify for QMB, you also qualify for Extra Help (see the final section).
Specified Low-Income Medicare Beneficiary (SLMB) Program
Monthly income and resource limits for the SLMB Program are:
- Filing individually: $1,379 monthly income; $8,400 in resources
- Married filing jointly: $1,851 monthly income; $12,600 in resources
This program helps pay your Medicare Part B premium.
If you qualify for SLMB, you also qualify for Extra Help (see the final section).
Qualifying Individual (QI) Program
Monthly income and resource limits for the QI Program are:
- Filing individually: $1,549 monthly income; $8,400 in resources
- Married filing jointly: $2,080 monthly income; $12,600 in resources
The program helps pay your Medicare Part B premium.
If you qualify for QI, you also qualify for Extra Help (see the final section).
Qualified Disabled and Working Individuals (QDWI) Program
The QDWI Program is available if at least one of the following is true for you:
- You are under age 65 and have a disability
- You had premium-free Part A but lost it when you returned to work
- Your state does not provide you with medical assistance
- You meet your state's income and resource limits
Monthly income and resource limits for the QDWI Program are:
- Filing individually: $4,615 monthly income; $4,000 in resources
- Married filing jointly: $6,189 monthly income; $6,000 in resources
The program helps pay your Medicare Part A premium.
Income Limits for Extra Help
The Extra Help program provides assistance paying Medicare prescription drug costs. It is available to Medicare beneficiaries who have limited income and resources. If you qualify for Medicaid, QMB, SLMB, or QI, you are automatically eligible for Extra Help.
If you qualify for Extra Help, you should receive a notice from Social Security. There are different levels of assistance, though. Talk to your Medicare prescription drug plan to determine whether you're paying the right amount. You can also contact Medicare at 1-800-MEDICARE (633-4227) if you think you qualify but have not received notification from Social Security.
Additional resources
Initial IRMAA Determination
External Website Link
Find Your Level of Extra Help (Part D)
External Website Link
Contact Your State with Questions
External Website Link
How to Qualify for a Medicare Savings Program
Internal Website Link